Observer 模式 (观察者模式 / 发布-订阅)
一个发布者(主题), 多个订阅者(观察者), 发布者发布消息通知所有订阅者.
例子
– 消息等发布-订阅
– MVC 是观察者模式的一种实现
– 常见的一个例子: 对同一组数据进行统计分析时候, 希望提供多种形式的表示,
(例如以表格进行统计显示, 柱状图统计显示和百分比统计显示等).
这些表示都依赖于同一组数据, 当数据改变的时候, 所有的统计的显示都能够改变.
认识观察者模式
认识观察者模式:

发布者(主题) + 订阅者(观察者) = 观察者模式:

观察者模式:
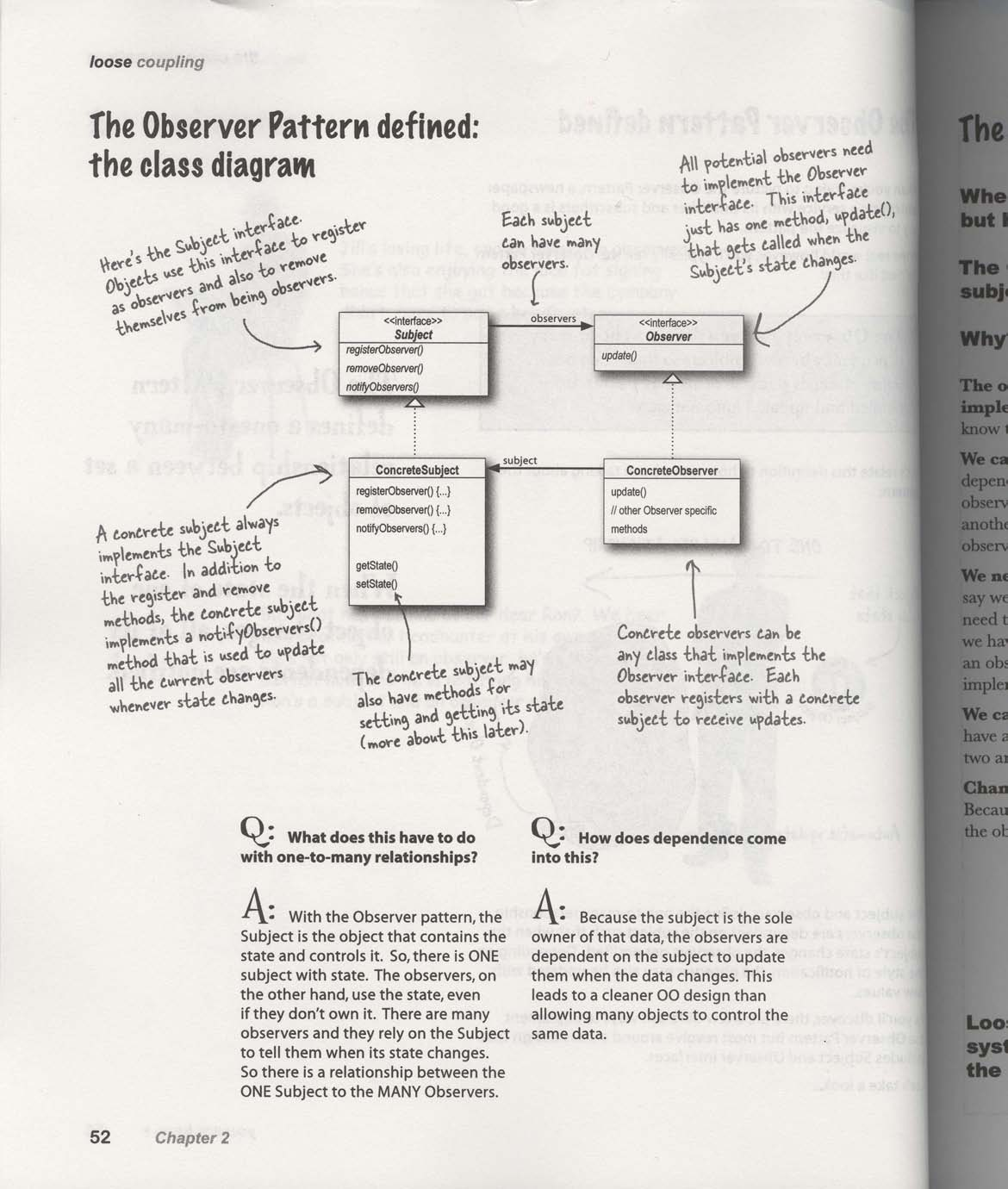
定义观察者模式
观察者模式 Observer pattern 定义了对象之间的一 (Subject or Topic) 对
多 (Observers) 的依赖关系.
这样一来, 当主题对象改变状态时, 它的所有依赖者都会收到通知并自动更新.
观察者模式 也称为发布-订阅 (Publish-Subscribe),
“主题 Subject” 就是消息的发布者(Publisher), “观察者 Observers”则是消息的订阅者
(Subscribers)
观察者模式应该可以说是应用最多, 影响最广的模式之一,
也是在大型系统开发过程中要用到的模式之一.
观察者的一个实例 Model / View / Control (MVC) 结构在系统开发架构设计中有着很重要的
地位和意义, MVC 实现了业务逻辑和表示层的解耦.
在 Java Struts 则提供和 MFC 中 Doc/View 结构类似的实现 MVC 的框架,
另外 Java 语言本身就提供了观察者模式的实现接口.
观察者模式类图示例
实现示例 1 分析
https://yuiwong.org/gitlab/cpp/cppprogdesipatt/tree/master/src/observer/example
/**
* 简单的观察者模式(主题 即发布者, 观察者即订阅者)实现
* g++ observer.cpp -std=c++11 -Wall -Wextra
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <functional>
#include <set>
template<typename T> struct Observer;
/**
* @struct Subject
* A generic subject(i.e. publisher) implementation
*/
template<typename T>
struct Subject {
using ObserverConstPtr = std::shared_ptr<Observer<T> const>;
Subject() noexcept = default;
virtual ~Subject() noexcept = default;
virtual bool subscribe(ObserverConstPtr const& observer) noexcept;
virtual bool unsubscribe(ObserverConstPtr const& observer) noexcept;
virtual bool publish(std::shared_ptr<T const> const& message) const
noexcept;
protected:
virtual void notify() const noexcept;
std::set<ObserverConstPtr> observers;
mutable std::shared_ptr<T const> message;
};
/**
* @struct Observer
* Basic and generic observer(i.e. subscriber) implementation
*/
template<typename T>
struct Observer {
Observer(
std::function<void(std::shared_ptr<T const> const&)> const& callback)
noexcept;
protected:
Observer() noexcept = default;
public:
virtual ~Observer() noexcept = default;
virtual void update(std::shared_ptr<T const> const& message) const
noexcept;
protected:
std::function<void(std::shared_ptr<T const> const&)> callback;
};
template<typename T>
bool Subject<T>::subscribe(ObserverConstPtr const& observer) noexcept
{
if (observer) {
auto const ret = this->observers.insert(observer);
return ret.second;
}
return false;
}
template<typename T>
bool Subject<T>::unsubscribe(ObserverConstPtr const& observer) noexcept
{
auto const it = this->observers.find(observer);
if (it != this->observers.end()) {
this->observers.erase(observer);
return true;
}
return false;
}
template<typename T>
bool Subject<T>::publish(std::shared_ptr<T const> const& message) const
noexcept
{
if (message) {
this->message = message;
this->notify();
return true;
}
return false;
}
template<typename T>
void Subject<T>::notify() const noexcept
{
for (auto it = this->observers.cbegin(), end = this->observers.cend();
it != end; ++it) {
(*it)->update(this->message);
}
}
template<typename T>
Observer<T>::Observer(
std::function<void(std::shared_ptr<T const> const&)> const& callback)
noexcept: callback(callback) {}
template<typename T>
void Observer<T>::update(std::shared_ptr<T const> const& message) const
noexcept
{
if (this->callback) {
this->callback(message);
}
}
/// String subscriber
struct SSubsciber {
SSubsciber();
void callback(std::shared_ptr<std::string const> const& a);
protected:
static int nextIdx;
int idx;
};
int SSubsciber::nextIdx = 0;
SSubsciber::SSubsciber(): idx(SSubsciber::nextIdx++) {}
void SSubsciber::callback(std::shared_ptr<std::string const> const& a)
{
std::cout << "SSubsciber." << this->idx << ": " << *a << "\n";
}
struct SObserver: public Observer<std::string> {
SObserver(): Observer() {
this->Observer::callback = std::bind(
&SObserver::callback, this, std::placeholders::_1);
}
void callback(std::shared_ptr<std::string const> const& a) const {
std::cout << "SObserver: " << *a << "\n";
}
};
struct S2Observer: public Observer<std::string> {
S2Observer(): Observer() {
this->Observer::callback = std::bind(
&S2Observer::callback, this, std::placeholders::_1);
}
void callback(std::shared_ptr<std::string const> const& a) const {
std::cout << "S2Observer: " << *a << "\n";
}
};
int main()
{
Subject<std::string> sPublihser;
std::shared_ptr<Observer<std::string> const> const sSubsciber1(
new Observer<std::string>([](std::shared_ptr<
std::string const> const& a){
std::cout << "aSubsciber1: " << *a << "\n";
}));
std::shared_ptr<Observer<std::string> const> const sSubsciber2(
new Observer<std::string>([](std::shared_ptr<
std::string const> const& a){
std::cout << "aSubsciber2: " << *a << "\n";
}));
SSubsciber ss3;
SSubsciber ss4;
std::shared_ptr<Observer<std::string> const> const s3(
new Observer<std::string>(std::bind(
&SSubsciber::callback, &ss3, std::placeholders::_1)));
std::shared_ptr<Observer<std::string> const> const s4(
new Observer<std::string>(std::bind(
&SSubsciber::callback, &ss4, std::placeholders::_1)));
std::shared_ptr<SObserver const> const s5(new SObserver());
std::shared_ptr<S2Observer const> const s6(new S2Observer());
sPublihser.subscribe(sSubsciber1);
sPublihser.subscribe(sSubsciber2);
sPublihser.subscribe(s3);
sPublihser.subscribe(s4);
sPublihser.subscribe(s5);
sPublihser.subscribe(s6);
auto const msg1 = std::shared_ptr<std::string>(new std::string("aaa"));
auto const msg2 = std::shared_ptr<std::string>(new std::string("bbb"));
sPublihser.publish(msg1);
sPublihser.publish(msg2);
std::cout << "\n";
sPublihser.unsubscribe(sSubsciber1);
sPublihser.publish(msg1);
sPublihser.publish(msg2);
return 0;
}
这里的主题提供依赖于它的观察者的注册和注销操作,
并且提供了使得依赖于它的所有观察者的通知操作. 观察者则提供一个 update 操作.
在观察者模式的示例实现中主题维护一个 unordered_set 作为存储其所有观察者的容器,
每当调用 notify 操作就遍历 set 中的观察者对象, 广播通知观察者 (调用观察者的 update).
运行示例程序, 可以看到当主题发布 aaa 和 bbb 的时候,
所有观察者都收到了 aaa 和 bbb, 然后第一个观察者取消订阅后,
再次发布 aaa 和 bbb 时除了第一个观察者其他都收到了.